In recent weeks, Bihar and Tamil Nadu have witnessed a string of hooch tragedies that have claimed the lives of over 50 individuals. These distressing incidents prompt a critical question: What makes hooch, an illegal and unregulated alcoholic beverage, more lethal than its legally sold counterparts? By delving into the chemistry behind hooch, we can uncover the stark differences between the alcohols used and the biochemical reactions they trigger upon consumption. Understanding these nuances is crucial in comprehending why hooch poses such grave risks to human health.
The Distinction between Ethanol and Methanol HOOCH:
The primary distinction lies in the types of alcohol employed. While legal alcoholic beverages contain ethyl alcohol, commonly known as ethanol, hooch often substitutes it with methyl alcohol, or methanol. Ethanol is derived through the fermentation of food crops and is utilized in both alcoholic beverages and pharmaceutical preparations. In contrast, methanol is primarily manufactured synthetically for industrial purposes, finding applications in acrylic plastics, synthetic fabrics, paints, and various other products. Methanol is also present in hand sanitizers, which underlines the serious hazards associated with its consumption. The preference for methanol in hooch production stems from its cost-effectiveness compared to ethanol.
 Toxicity Differences:
Toxicity Differences:
When consumed, even a small quantity of methanol can be highly toxic. The Food Safety and Standards (Alcoholic Beverages Standards) Regulation, 2018, stipulates limits on methanol usage in alcoholic beverages, with the threshold set at 50 grams per 100 liters for country liquor. It is important to note that methanol itself does not directly cause the damaging effects on the eyes, blindness, or death. Instead, these outcomes arise from the formation of new compounds when the body metabolizes methanol.
Understanding Alcohol Metabolism:
Upon consumption, alcohol undergoes two essential processes within the body. Firstly, enzymes in the body break down alcohol into various compounds, each of which affects health differently. Secondly, excessive alcohol intake leads to the entry of alcohol into the bloodstream and eventually reaches the brain, resulting in intoxication. The extent of intoxication depends on factors such as the quantity consumed and the body’s ability to process alcohol.
The Effects of Methanol:
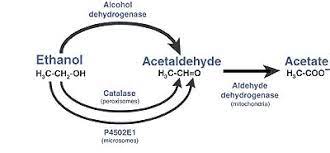
Methanol’s breakdown follows a two-step process: Alcohol Dehydrogenase (ADH) reacts with methanol to produce formaldehyde, and subsequently, Aldehyde Dehydrogenase (ALDH) reacts with formaldehyde to form formic acid. Both formaldehyde and formic acid are highly toxic compounds. Formaldehyde can cause corrosion of the oesophagus and stomach, leading to ulcers, vomiting, diarrhea, and inflammation. Inhalation of formaldehyde vapor can induce dizziness or suffocation, while contact with formaldehyde solution can result in severe burns to the eyes and skin. Formic acid, on the other hand, can cause burns to the skin and eyes, potentially leading to blindness. It may also lead to fluid accumulation in the lungs, posing further health risks.
The Effects of Ethanol:
In the case of ethanol, ADH reacts with it to form acetaldehyde, which can cause symptoms such as headaches, nausea, increased heart rate, and hangovers. Prolonged exposure to high levels of acetaldehyde can potentially lead to stomach and intestinal cancer. However, the risk is mitigated by the second stage of metabolism, wherein the ALDH enzyme converts acetaldehyde into acetic acid, which is non-toxic. Some individuals may have a lower ability to metabolize acetaldehyde, making them more susceptible to long-term risks.
In conclusion, the chemistry behind hooch tragedies unveils a stark reality of the dangers posed by illicit liquor. The use of methanol instead of ethanol in hooch production leads to devastating consequences, with even small quantities proving fatal. To combat the hooch crisis, it is essential to prioritize public health and safety, strengthen law enforcement measures, raise awareness, provide support for addiction recovery, address socioeconomic factors, and collaborate with international partners. By working together, we can strive to eliminate the tragic loss of lives caused by hooch and ensure a safer and healthier future for all.
Additionally, effective regulation and monitoring systems should be put in place to ensure the safety and quality of legally produced alcoholic beverages. Strict adherence to standards and regular inspections of manufacturing facilities can help prevent the adulteration or contamination of alcoholic products. This includes enforcing limits on methanol content in alcoholic beverages and conducting thorough quality control checks to identify any potential risks.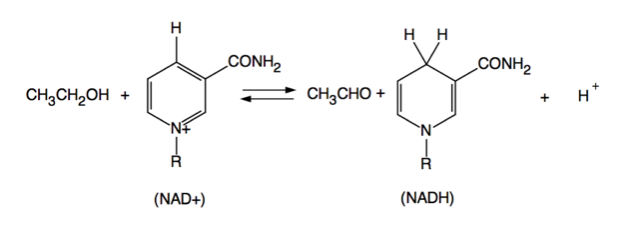
Public health campaigns should focus on educating individuals about the dangers of consuming hooch and the potential health consequences they may face. Emphasizing the immediate and long-term risks associated with methanol consumption can deter people from seeking out illicit liquor. These campaigns should target not only the general public but also vulnerable communities where the prevalence of hooch consumption may be higher.
Furthermore, initiatives aimed at promoting the production and distribution of legal alcoholic beverages can contribute to reducing the demand for hooch. This can involve supporting local breweries, wineries, and distilleries that comply with safety regulations and produce high-quality alcoholic beverages. Encouraging responsible drinking practices and creating a positive social environment around legal alcohol consumption can help shift consumer preferences away from illicit sources.
Engagement with local communities is crucial for effectively addressing the hooch problem. Community-based organizations, NGOs, and grassroots initiatives can play a significant role in raising awareness, providing support services, and advocating for stronger regulations. By empowering communities to take ownership of their health and well-being, sustainable solutions can be developed that address the unique challenges and circumstances of each region.
In terms of law enforcement, it is vital to enhance intelligence gathering and surveillance to identify and dismantle hooch manufacturing operations. This requires a comprehensive approach that involves collaboration between local police departments, state agencies, and national law enforcement bodies. Sharing information, coordinating efforts, and conducting targeted raids can disrupt the illicit hooch trade and bring the culprits to justice.
Simultaneously, it is essential to provide alternative livelihood opportunities for those involved in the illegal production and sale of hooch. Creating vocational training programs, supporting entrepreneurship, and offering financial incentives can help individuals transition away from the illicit liquor trade and engage in legal and sustainable economic activities.Moreover, public-private partnerships can play a crucial role in addressing the hooch crisis. Collaborating with alcohol industry stakeholders, such as producers, distributors, and retailers, can ensure responsible practices, promote consumer safety, and support initiatives aimed at curbing the consumption of hooch.